Predložak:Chess diagram/doc
Ovo je dokumentacijska podstranica za Predložak:Chess diagram. Sadrži informacije o uporabi, kategorijama i ostalom sadržaju koji nije dio izvornog predloška |
| Koristi Lua modul: |
These templates shows a chess diagram, a graphic representation of a position in a chess game, using standardised symbols resembling the pieces of the standard Staunton chess set. The default template for a standard chess board is {{Chess diagram}}. This documentation covers all related templates.
Syntax
[uredi kôd]The syntax is basically the same for all chess diagram templates.
{{Chess diagram
| <alignment> (param #1)
| <header> (#2)
| size =
| numbers =
| letters =
| <a8> | <b8> | ... | <h8> (#3 to ...
| <a7> | <b7> | ... | <h7>
...
| <a1> | <b1> | ... | <h1> ( ... #66)
| <footer> (#67)
| reverse =
}}
Parameters:
<alignment>– defines horizontal alignment (floating) of the whole table, must betrightortleft(or nothing)<header>– the text which appears above the diagram, may be empty;size- specifies the size of each square in pixels, the default is 26.numbers- specifies whether the rows are numbered. Options are: left, right, both (default) or neither.letters- specifies whether the columns are lettered. Options are: top, bottom, both (default) or neither.<a8>, <b8>, ... <h1>– define corresponding squares of the chessboard, see below;<footer>– the text which appears beneath the diagram, may be empty; optional – can be left out (currently not in the other templates)
A square is defined by the name of piece or empty parameter. The names of the pieces are those given in algebraic notation:
These letters are combined with either "l" for Light=White, or "d" for Dark=Black. So "kl" is White's king, and "nd" is Black's knight.
An empty square is written either using underscores, spaces, or nothing at all. Two spaces are recommended.
Fairy Chess
[uredi kôd]There are also some fairy chess pieces available:



 a = archbishop (Princess)
a = archbishop (Princess)


 c = chancellor (Empress)
c = chancellor (Empress)


 f = inverted king (Mann)
f = inverted king (Mann)


 g = inverted queen (Grasshopper)
g = inverted queen (Grasshopper)


 m = inverted rook (Dabbaba, Threeleaper or Wazir)
m = inverted rook (Dabbaba, Threeleaper or Wazir)


 j(e) = elephant (Alfil or Ferz)
j(e) = elephant (Alfil or Ferz)


 N(s) = inverted knight (Camel, Kirin, Nightrider or Phoenix)
N(s) = inverted knight (Camel, Kirin, Nightrider or Phoenix)


 h = inverted pawn (Berolina pawn)
h = inverted pawn (Berolina pawn)


 M = Mann (alternate symbol)
M = Mann (alternate symbol)
 C = Centaur or Amazon
C = Centaur or Amazon
Omega Chess pieces:
Other suitable images include:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Other symbols
[uredi kôd]You can also use "xx" for a black cross, "ox" for a white cross, "xo" for a black circle on an empty square or "oo" for a white one.
When showing movement directions on the board, arrows are available

 ul = up & left
ul = up & left
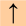 ua = up
ua = up
 ur = up & right
ur = up & right
 la = left
la = left
 lr = left & right
lr = left & right
 ud = up & down
ud = up & down
 ra = right
ra = right
 dl = down & left
dl = down & left
 da = down
da = down
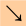 dr = down & right
dr = down & right
Numbers can also be added to squares by using "x0" for 0, "x1" for 1, "x2" for 2, ..., "x9" for 9.
Examples
[uredi kôd]Standard diagram
[uredi kôd]This diagram is recommended for common use as a main diagram in the articles on chess openings, endings, games, positions etc. See the corresponding code below.
| a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | ||
| 8 |  | 8 | |||||||
| 7 | 7 | ||||||||
| 6 | 6 | ||||||||
| 5 | 5 | ||||||||
| 4 | 4 | ||||||||
| 3 | 3 | ||||||||
| 2 | 2 | ||||||||
| 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | ||
{{Chess diagram
| tright
|
|rd|nd|bd|qd|kd|bd|nd|rd
|pd|pd|pd|pd| |pd|pd|pd
| | | | | | | |
| | | | |pd| | |
| | | | |pl|pl| |
| | | | | | | |
|pl|pl|pl|pl| | |pl|pl
|rl|nl|bl|ql|kl|bl|nl|rl
| The King's Gambit
}}
| a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | ||
| 8 |  | 8 | |||||||
| 7 | 7 | ||||||||
| 6 | 6 | ||||||||
| 5 | 5 | ||||||||
| 4 | 4 | ||||||||
| 3 | 3 | ||||||||
| 2 | 2 | ||||||||
| 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | ||
{{Chess diagram
| tright
|
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| Empty board
}}
Diagram with both captions
[uredi kôd]| a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | ||
| 8 |  | 8 | |||||||
| 7 | 7 | ||||||||
| 6 | 6 | ||||||||
| 5 | 5 | ||||||||
| 4 | 4 | ||||||||
| 3 | 3 | ||||||||
| 2 | 2 | ||||||||
| 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | ||
This problem uses partial retrograde analysis method.
It may be convenient to use this in the articles on chess problems. Please note that in the header and footer you can use bolds or italics. You can also use <br> to break the lines.
{{Chess diagram
| tright
| '''W. Langstaff''', ''Chess Amateur'' 1922
| | | | |kd| | |rd
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | |bl| |pl
| | | |rl| |kl|pd|pl
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| '''Mate in two.''' <br> This problem uses ''partial retrograde analysis'' method.
}}
Diagram without captions
[uredi kôd]| a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | ||
| 8 |  | 8 | |||||||
| 7 | 7 | ||||||||
| 6 | 6 | ||||||||
| 5 | 5 | ||||||||
| 4 | 4 | ||||||||
| 3 | 3 | ||||||||
| 2 | 2 | ||||||||
| 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | ||
See the corresponding code below. If you don't want the captions, just remove them, but don't delete the second "|" pipe character for the caption above; it is possible to delete the last pipe for the longer caption below.
The diagram floats to the left to illustrate the use of the first parameter.
{{Chess diagram
| tleft
|
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| |xx|xo|xx| | | |
| | |pl| | | | |
| | | | | |xo| |
| | | | |xx|xo|xx|
| | | | | |pl| |
| | | | | | | |
}}
Movement example
[uredi kôd]This can be used to show how pieces move.
| a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | ||
| 8 |  | 8 | |||||||
| 7 | 7 | ||||||||
| 6 | 6 | ||||||||
| 5 | 5 | ||||||||
| 4 | 4 | ||||||||
| 3 | 3 | ||||||||
| 2 | 2 | ||||||||
| 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | ||
any direction, but only one square, while black rook can move any number of squares but only up and down, and right and left.
{{Chess diagram
| tleft
|
| | |ua| | | | |
| | |ua| | | | |
|la|la|rd|ra|ra|ra|ra|ra
| | |da| | | | |
| | |da| |ul|ua|ur|
| | |da| |la|kl|ra|
| | |da| |dl|da|dr|
| | |da| | | | |
|Example showing how white king can move
any direction, but only one square, while
black rook can move any number of squares
but only up and down, and right and left.
}}
| a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | ||
| 8 |  | 8 | |||||||
| 7 | 7 | ||||||||
| 6 | 6 | ||||||||
| 5 | 5 | ||||||||
| 4 | 4 | ||||||||
| 3 | 3 | ||||||||
| 2 | 2 | ||||||||
| 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | ||
{{Chess diagram
| tright
|
| |ul| |ua| |ur| |
| | |ul|ua|ur| | |
|la|la|la|ql|ra|ra|ra|ra
| | |dl|da|dr| | |
| |dl| |da| |dr| |
|dl| | |da| | |dr|
| | | |da| | | |dr
| | | |da| | | |
}}
In the board on the right, it is shown that the white queen can go any distance in any of these directions.
Another method for the rook example:
| a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | ||
| 8 |  | 8 | |||||||
| 7 | 7 | ||||||||
| 6 | 6 | ||||||||
| 5 | 5 | ||||||||
| 4 | 4 | ||||||||
| 3 | 3 | ||||||||
| 2 | 2 | ||||||||
| 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | ||
{{Chess diagram
| tleft
|
| | | | | | | |
| | |ud| | | | |
| |lr|rd|lr| | | |
| | |ud| | | | |
| | | | |ul|ua|ur|
| | | | |la|kl|ra|
| | | | |dl|da|dr|
| | | | | | | |
}}
Alternative way to place the pieces: FEN
[uredi kôd]{{Chess diagram|fen=rnbqkbnr/pppppppp/8/8/8/8/PPPPPPPP/RNBQKBNR|align=tleft}}
| a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | ||
| 8 |  | 8 | |||||||
| 7 | 7 | ||||||||
| 6 | 6 | ||||||||
| 5 | 5 | ||||||||
| 4 | 4 | ||||||||
| 3 | 3 | ||||||||
| 2 | 2 | ||||||||
| 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | ||
It is possible to populate the board using Forsyth–Edwards Notation, instead of positional parameters.
To do this, the "fen" parameter is used. For instance, this is the opening board of a chess game, defined using the "fen" parameter "rnbqkbnr/pppppppp/8/8/8/8/PPPPPPPP/RNBQKBNR":
{{Chess diagram|fen=rnbqkbnr/acfghzwt/8/8/8/8/ACFGHZWT/RNBQKBNR|align=tleft}}
| a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | ||
| 8 |  | 8 | |||||||
| 7 | 7 | ||||||||
| 6 | 6 | ||||||||
| 5 | 5 | ||||||||
| 4 | 4 | ||||||||
| 3 | 3 | ||||||||
| 2 | 2 | ||||||||
| 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | ||
It is also possible to show "fairy" pieces using the FEN notation. However, because the FEN notation uses uppercase and lowercase to denote the color of the piece, it is not possible to display the inverted knight fairy piece (denoted by "N") using the fen parameter. Here is a board where the pawns are replaced by fairy pieces:
Only 8x8 boards can use the "fen" parameter. For other size boards, positional parameters should be used.
Displaying the board from the Black's point of view
[uredi kôd]{{Chess diagram|fen=rnbqkbnr/pppppppp/8/8/8/8/PPPPPPPP/RNBQKBNR|align=tleft|reverse=true}}
| h | g | f | e | d | c | b | a | ||
| 1 |  | 1 | |||||||
| 2 | 2 | ||||||||
| 3 | 3 | ||||||||
| 4 | 4 | ||||||||
| 5 | 5 | ||||||||
| 6 | 6 | ||||||||
| 7 | 7 | ||||||||
| 8 | 8 | ||||||||
| h | g | f | e | d | c | b | a | ||
The "reverse=true" parameter causes the board to be shown from Black's point of view, that is, with the h8 square at lower-left corner, and a1 at the upper-right. This works for all sizes of the normal chessboard template, but not for the Alice, Bughouse, Omega, or Raumschach templates. Here, the same FEN notation as in the previous example produces a board with Black's starting position at the bottom.
